A. V
B. 2V
C. 1/2 V
D. Zero
E. Cannot be determined
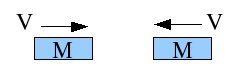
Two cars of equal mass are traveling opposite directions at speed V. The collide completely elastically. The final speed of the vehicle on the left is
A. V to the right
B. 2V to the right
C. V to the left
D. 2V to the left
E. zero
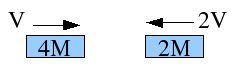
Two cars of unequal mass are traveling opposite directions as indicated. The collide inelastically and stick together. The final speed of the combined vehicle is
A. V to the right
B. 2V to the right
C. V to the left
D. 2V to the left
E. zero
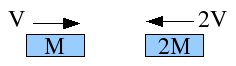
Two cars of unequal equal mass are traveling opposite directions as indicated. The collide inelastically and stick together. The final speed of the combined vehicle is
A. V to the left
B. 2V to the left
C. 2/3V to the left
D. 3/2V to the left
E. zero
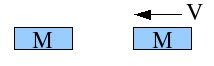
A car of mass M traveling to the left collides with a car of mass M initially stationary but free to move. The collide inelastically and stick together. The final speed of the combined vehicle is
A. V to the left
B. 2V to the left
C. 1/2V to the left
D. 3/2V to the left
E. zero

A car of mass M traveling to the left collides with a car of mass M initially stationary but free to move. The collide completely elastically. The car initially on the left
A. remains stationary
B. moves off to the left with speed 1/2 V
C. moves off to the left with speed V
D. moves off to the left with speed 3/2 V
E. moves off to Fresno to live with great Aunt Ruth
What if the mass of the moving car were 2M instead? Solve this as a group. (may take a little while...)

Two joined cars of mass M and 2M are at rest liked by a compressed spring that is released. After the spring fires, one car moves off to the right and the other to the left. The car initially on the left has a speed that is
A. zero
B. equal to the one on the right
C. one half the speed on the right
D. twice the one on the right
E. warp nine

Two joined cars of mass M traveling to the right at speed 2V are liked by a compressed spring that is released. After the spring fires, one car moves off to the right with speed 4V. The car initially on the left
A. remains stationary
B. moves off to the left with speed 1/2 V
C. moves off to the left with speed V
D. moves off to the left with speed 3/2 V
E. moves off at warp factor seven
Is kinetic energy conserved in this event? Why or why not?
 Two joined cars of mass M and 2M are at rest
liked by a compressed spring that is released.
After the spring fires, one car moves off to the right and the
other to the left. Find the position of the center of mass
when the cars are separated by 1 meter. Answer as a distance
in m from the car on the left.
Two joined cars of mass M and 2M are at rest
liked by a compressed spring that is released.
After the spring fires, one car moves off to the right and the
other to the left. Find the position of the center of mass
when the cars are separated by 1 meter. Answer as a distance
in m from the car on the left.
What is the speed of the center of mass?
Two objects collide inelastically. Can all of the initial kinetic energy in the collision be converted into other forms of energy?
A. Yes, but only for certain special initial conditions
B. Yes, provided that the objects are soft enough
C. No, this violates a fundamental law of physics
D. None of the above
An object of mass 10M traveling to the left at speed V collisdes elastically with an object of mass M
traveling to the right at speed V. After the collision the speed of the less massive object is
A. Zero
B. less than V to the left
C. V to the left.
D. >V to the left.
A. Zero
B. less than V to the left
C. V to the left.
D. >V to the left.